Asp.Net MVC HTTP Error 401.0 - Unauthorized
Posted on: 2012-11-16
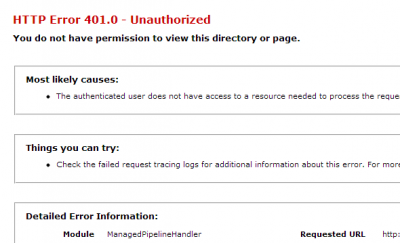
HTTP Error 401.0 - Unauthorized You do not have permission to view this directory or page.
When an unauthorized action is trigged, the HttpUnauthorizedResult result called. It produces a 401 error. By default, a 401 error can be handled only by IIS and not directly like a 404 error with Asp. This would be easy if we could set a 401 error page in the web.config, but it's not the case.
namespace System.Web.Mvc {
public class HttpUnauthorizedResult : HttpStatusCodeResult {
// HTTP 401 is the status code for unauthorized access. Other code might
// intercept this and perform some special logic. For example, the
// FormsAuthenticationModule looks for 401 responses and instead redirects
// the user to the login page.
private const int UnauthorizedCode = 401;
public HttpUnauthorizedResult() : this(null) { }
public HttpUnauthorizedResult(string statusDescription) : base(UnauthorizedCode, statusDescription) { }
}
}
// File provided for Reference Use Only by Microsoft Corporation (c) 2007.
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
What can be done is to transform the 401 error code into a standard code, like the 200 code. This response header code indicate that the webpage has been found. This will let us counter the 401 behaviors and redirect to a specific actions.
public abstract class HttpUnauthorizedWithRedirectToResultBase : HttpUnauthorizedResult {
protected ActionResult_result;
public override void ExecuteResult(System.Web.Mvc.ControllerContext context) {
if (context == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("context");
if (context.HttpContext.Request.IsAuthenticated) {
context.HttpContext.Response.StatusCode = 200;
InitializeResult(context);_result.ExecuteResult(context);
}
else
base.ExecuteResult(context);
}
protected abstract void InitializeResult(ControllerContext context); }
We will create a new http unauthorized that will set area and view name. This will let us set the default page if we do not want to specify every time which action to use. If nothing will be defined, we will be able to simply put in the shared folder a view with the error.
public class HttpUnauthorizedWithRedirectToViewResult : HttpUnauthorizedWithRedirectToResultBase {
private readonly string_area; private readonly string_viewName;
public HttpUnauthorizedWithRedirectToViewResult(string viewName, string area) {
_viewName = viewName;
_area = area;
}
protected override void InitializeResult(ControllerContext context) {
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(_area)) {
context.RequestContext.RouteData.DataTokens["area"] =_area;
}
_result = new ViewResult{ViewName =_viewName};
}
}
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Method, Inherited = true, AllowMultiple = false)]
public class AuthorizeWith401Support : AuthorizeAttribute {
private const string VIEW_NAME = "NoAccess401";
private string_actionName;
public string ActionName {
get {
return string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(_actionName)? VIEW_NAME :_actionName;
}
set {
_actionName = value;
}
}
public string Controller { get; set; }
public string Area { get; set; }
protected override void HandleUnauthorizedRequest(AuthorizationContext filterContext) {
if (filterContext.IsChildAction) {
base.HandleUnauthorizedRequest(filterContext);
} else {
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(ActionName))
throw new ArgumentException("You must set an ActionName");
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(controller))
filterContext.Result = new HttpUnauthorizedWithRedirectToViewResult(ActionName, area);
}
}
}
Now, you need to use it as you would use the AuthorizeAttribute. It's the same behavior because the AuthorizeWith401Support inherit from AuthorizeAttribute. However, you have the additionnal ActionName, Area and Controller property that let you specify the error action. Of course, if nothing is specifie, the action NoAccess401 will be used.
[AuthorizeWith401Support(Roles = "admin")]
public ActionResult Index() {
//...
}
